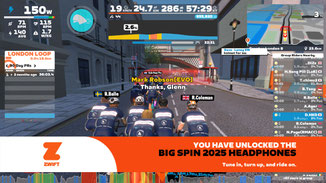
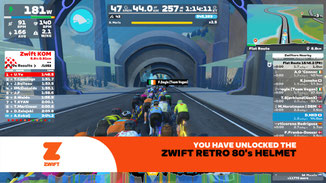
Modern virtual indoor training platforms like Zwift have significantly reconfigured the cycling experience. With the rise of smart trainers and immersive virtual environments, indoor cycling has evolved into a highly efficient, data-driven, and socially engaging form of training. It offers consistent workouts unaffected by weather, traffic, or daylight, making it ideal for riders with time constraints or specific performance goals. Research highlights benefits such as improved training efficiency, real-time performance tracking, and enhanced motivation through social community features like group rides and virtual races.
This page highlights the growing role of gamification in cycling through platforms like Zwift, which has transformed traditional training into an interactive and engaging digital experience. From an information systems perspective, Zwift presents a rich environment for research into user behaviour, motivation, and performance. The platform incorporates game mechanics such as achievement badges, levels, in-game rewards, and social leaderboards to enhance user engagement and encourage consistent participation. These elements provide valuable data on how digital feedback, community interaction, and immersive design influence cycling habits and training outcomes. Zwift offers opportunities to study the intersection of technology, sport, and user experience—ranging from performance analytics to the psychological effects of virtual competition and collaboration.
Zwift also offers significant benefits for health and inclusivity by creating a global cycling community that transcends geographical boundaries. As a virtual platform, it enables people of all fitness levels, ages, and locations to participate in cycling in a safe, accessible, and socially connected environment. This inclusivity supports regular physical activity for individuals who may face barriers to outdoor exercise, such as limited mobility, harsh weather, or lack of safe cycling infrastructure. Zwift promotes cardiovascular fitness, endurance, and mental well-being through structured training plans and engaging ride experiences. At the same time, its social features—such as group rides, live events, and community challenges—foster a sense of belonging and motivation, helping users stay committed to their health goals. By removing physical and social barriers, Zwift helps democratize access to cycling and supports a more diverse and connected global cycling culture.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly important role in enhancing the Zwift experience, offering new possibilities for personalized training, performance analysis, and user engagement. AI-driven algorithms can analyze a rider’s power data, heart rate, and performance history to generate tailored workouts and adaptive training plans that evolve with the user’s progress. Virtual training partners and bots powered by AI can simulate realistic pacing, race tactics, and group dynamics, allowing users to train in varied scenarios that reflect real-world cycling challenges. AI also helps optimize in-game matchmaking, route suggestions, and event recommendations, improving the overall user experience. From a broader perspective, Zwift’s use of AI opens up research opportunities in areas such as adaptive learning systems, digital coaching, and the development of intelligent feedback loops that enhance both athletic performance and user motivation in virtual fitness environments.
Students in systems information science can use the Zwift platform as a dynamic environment for a wide range of research applications. With its rich integration of real-time data, user interaction, and gamified design, Zwift offers opportunities to study human-computer interaction, data analytics, behavioural motivation, and the effectiveness of AI-driven training systems. Research can also focus on areas such as social network analysis within virtual communities, the impact of gamification on user retention, and the design of adaptive feedback systems for personalized health interventions. The platform’s global scope and accessibility make it ideal for cross-cultural studies and longitudinal data collection. Hakodate Cycle is active on Zwift and welcomes research collaborations through the platform, offering a unique bridge between academic inquiry and the evolving digital cycling ecosystem.